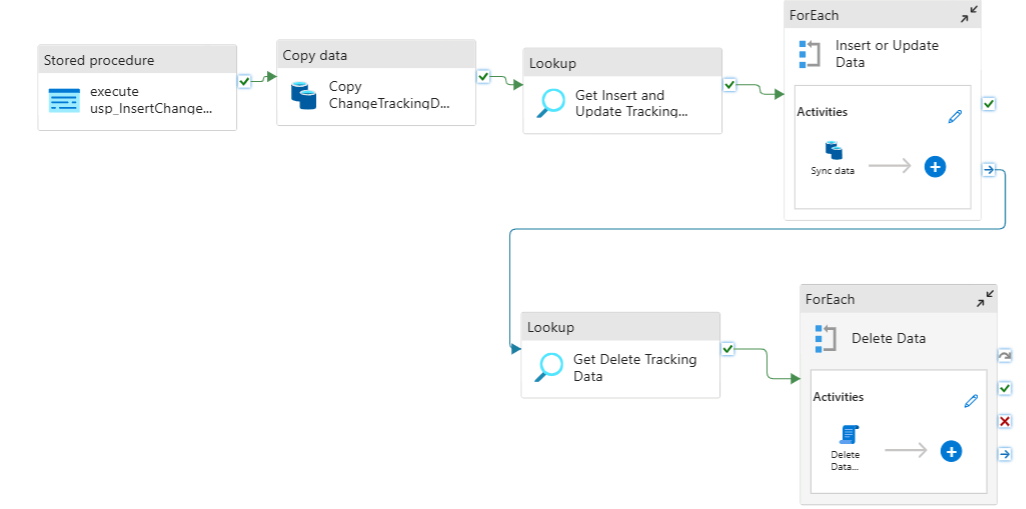
Upsert Strategy:
The pipeline uses the upsert operation to avoid duplication and ensure seamless data integration. By using the primary key, records are inserted if they don't exist or updated if they do.
Ordered Processing:
The use of OrderReference ensures that operations are executed in the correct sequence, preventing issues with foreign key dependencies.
Parallel and Sequential Execution:
Inserts and updates are processed sequentially to maintain data integrity.
Deletions are handled separately in reverse order to avoid constraint violations.
Timeout and Retry Policies:
Each activity has a timeout of 12 hours and no automatic retries, providing stability during large data migrations.