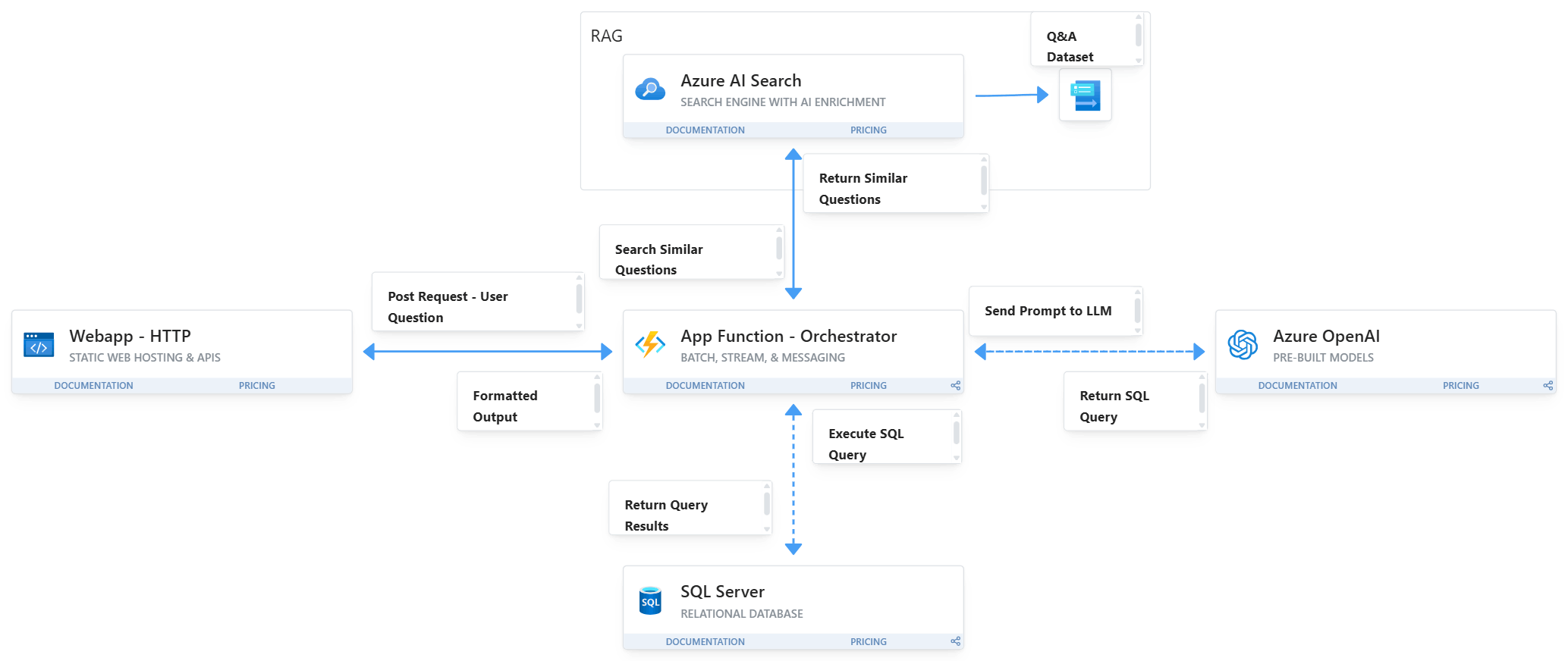
The assistant follows a multi-stage flow to ensure reliable and context-aware responses:
Step 1 – Session Management and Prompt Engineering
Each user request is tracked with session control to maintain conversational context. Prompts are structured according to task type (query generation, explanation, or analysis) and incorporate schema metadata to guide the LLM.
Step 2 – SQL Query Generation and Execution
When the user asks a question involving data extraction, the assistant generates a SQL query using strict formatting rules aligned with the Data Warehouse schema. The generated query is validated and executed against the SQL Server database, returning the result to the assistant.
Step 3 – Analytical or Descriptive Response
Based on the returned dataset, the assistant determines whether a simple response or a detailed analytical explanation is needed. In the case of larger or grouped datasets, it generates business-oriented summaries with actionable insights.
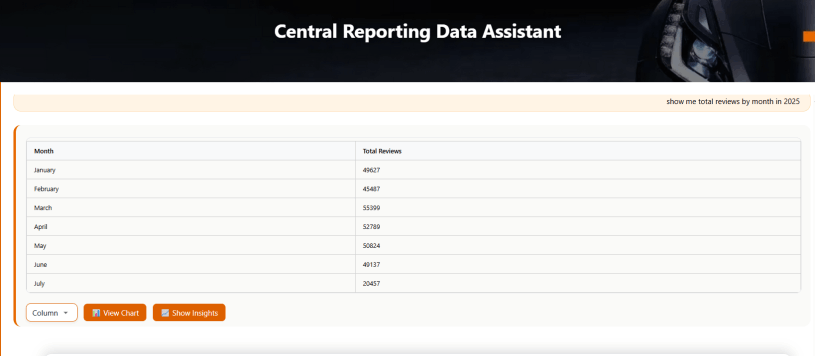
Step 4 – Result Display and Graph Options
The front-end interface renders the table results, and if the data meets graphable criteria (e.g., categorical vs. numeric values), the assistant suggests graphical visualizations. If analysis is available, a "Show Analysis" button is displayed to reveal insights.